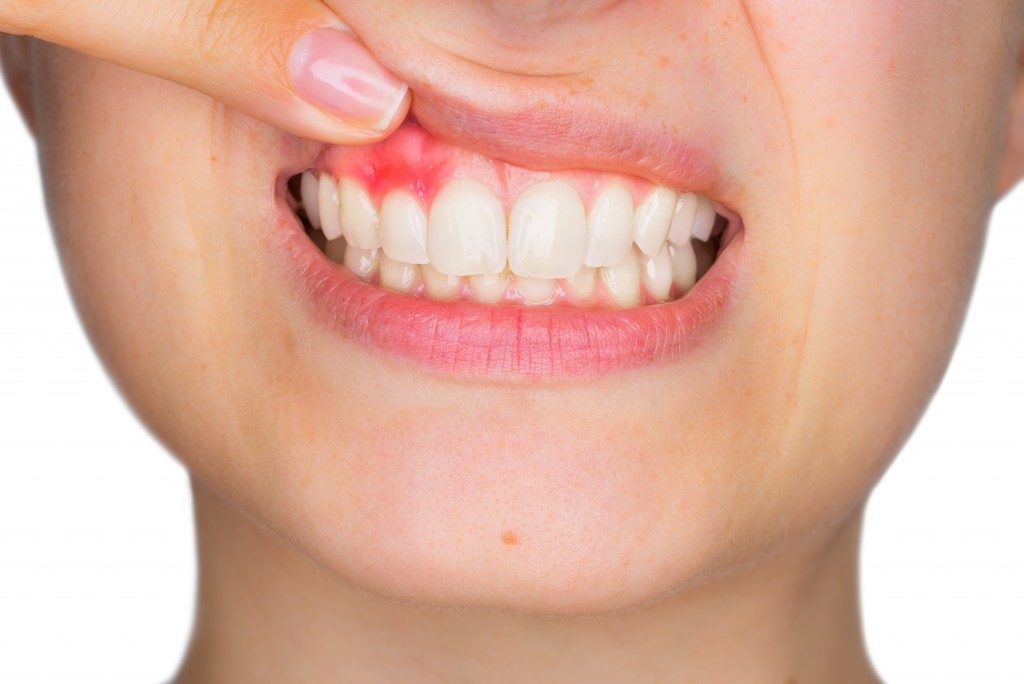
Gum disease is an infection that could lead to a host of health issues, such as tooth loss and severe gum damage, if left unaddressed. It has also been associated with a higher risk of developing heart disease and stroke, which, in turn, could negatively impact your overall health.
It can develop in spaces between the teeth and gum line, and cause inflammation in the tissue that can lead to the gums receding over time. Essentially, the severity of gum disease will be determined according to the pockets or excess space that develop due to the gum receding.
Different Kinds of Gum Disease
Gum disease is categorized as either periodontitis or gingivitis. The initial stage of gum disease, gingivitis, can be reversed with proper treatment. Left untreated, however, it can progress to more severe gum diseases like periodontitis.
Gingivitis is characterized by irritated and swollen gums that bleed more easily than undamaged gums. Proper oral health care practices such as brushing and flossing every single day and visiting your dentist regularly for dental cleanings can help prevent and reverse it.
Periodontitis is caused by untreated gingivitis. When you have periodontitis, you will notice your gums significantly receding from your teeth, which results in the development of infected gum pockets. But as your body starts to fight off this infection, the bones and tissues inside your mouth might begin to break down.
When this occurs, you should seek prompt treatment. Otherwise, the gums, jawbones and connective tissue that support the teeth might deteriorate and start to affect your oral health negatively. In time and without proper treatment, your teeth will become loose and will need to be removed or fall out on their own.
What Happens if You Do Not Treat Gum Disease?
Not treating gum disease is linked to a higher risk of stroke and heart disease. For women, it also increases the risk of giving birth to a baby who is premature or has a low birth weight. Furthermore, it has also been related to issues regulating blood sugar levels in those with diabetes.
How Is Gum Disease Treated?
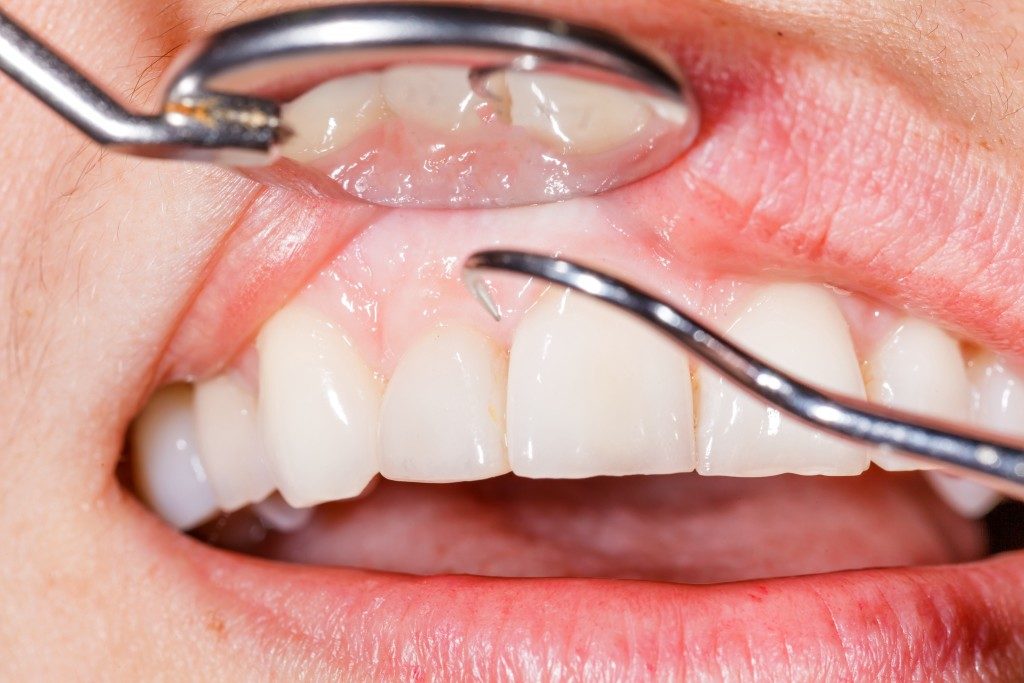
When you visit a dental clinic in Oviedo, Florida, your dentist will inform you of your treatment options based on what type of gum disease you have. Your dentist’s primary purpose is to treat the infection with one or more the following options:
- Medications
- Frequent professional dental cleanings
- For more serious cases, surgical intervention such as flap surgery might be required. This involves pulling the gum tissue up to get rid of tartar and stitching it back up to make it more fitted around your teeth. Your dentist can also use tissue grafts for replacing very damaged gum or bone as with bone grafting. With this procedure, a tiny mesh-like material will be placed between your gum and bone tissue to enable them to regenerate themselves.
While having different treatment options is fine and all, it is still better if you try and prevent gum disease from happening in the first place. It is quite simple really; brush and floss twice daily, visit your dentist for cleanings and exams, and eat a well-balanced diet.