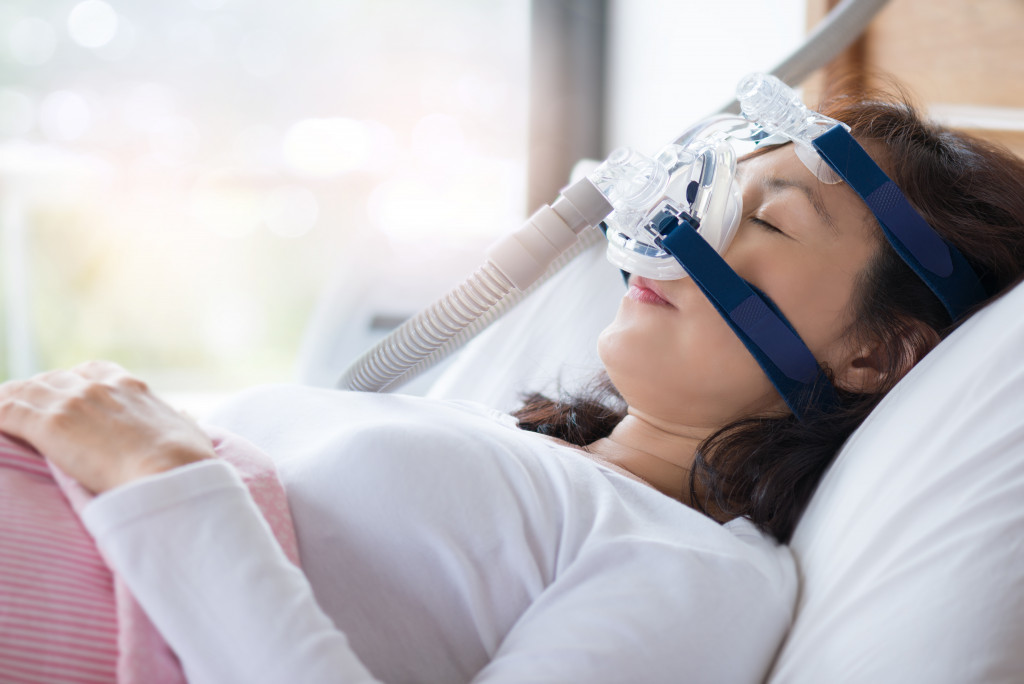
- Using a CPAP machine is an effective treatment for OSA diagnosis.
- Practicing good sleep hygiene can help improve your sleep quality and reduce your symptoms.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking can reduce your symptom severity.
- Regular screenings and tests can help monitor your OSA and determine the most effective treatment plan.
If you have recently been diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), you may feel overwhelmed and unsure of how to manage your condition. OSA is a common sleep disorder that causes disruptions in breathing during sleep, which can lead to a range of health issues if left untreated. However, proper management can reduce your symptoms and improve your overall health and well-being. This guide will provide five tips to help you manage your OSA diagnosis.
1. Use a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Machine
One of the most effective treatments for OSA is using a CPAP machine, which helps to keep your airway open during sleep. It is important to use your CPAP machine as your healthcare provider prescribes, as consistent use can help reduce symptoms such as snoring, daytime fatigue, and headaches. You may need to try different masks or pressure settings to find the most comfortable and effective option.
2. Practice Good Sleep Hygiene

In addition to using a CPAP machine, practicing good sleep hygiene can help to improve your sleep quality and reduce OSA symptoms. This includes establishing a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment. You may also want to consider using a wedge pillow or raising the head of your bed to reduce the likelihood of your airway becoming blocked during sleep.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can contribute to the development and severity of OSA. If you are overweight, losing even a small amount of weight can help to reduce your symptoms. This may involve making dietary changes, such as reducing your intake of processed foods, increasing your intake of fruits and vegetables, and engaging in regular physical activity.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking can worsen OSA symptoms and increase your risk of developing other respiratory conditions. If you smoke, quitting can be important in managing your OSA diagnosis. Many smoking cessation resources are available, including nicotine replacement therapies and support groups.
Talking to your doctor can also help you quit smoking. They can recommend medications and other strategies that will work best for you. Behavioral therapies, such as counseling, are important to quitting smoking, as they can provide support and coping skills. It is important to set reasonable goals and develop a plan that works for you so that you can gradually reduce your smoking.
5. Get Regular Screenings
Regular screenings can help monitor your OSA symptoms and ensure your treatment plan is effective. You may need to undergo a sleep study or other diagnostic tests to assess the severity of your condition and determine the best course of treatment. Working closely with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive management plan that addresses your individual needs and preferences is important.
Here are some screenings and tests you should get:
Sleep Study
A sleep study is performed in a laboratory and can help determine the severity of your OSA. During the study, your breathing, heart rate, and oxygen levels are monitored to assess how often you stop breathing during sleep and for how long.
Imaging Tests

Depending on the symptoms and severity of your OSA, imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans may be recommended to observe any anatomical changes in your airway. An open upright MRI is also a great alternative for claustrophobic people due to its wide open design and lack of confined space. This type of MRI will allow for a detailed look at your head and neck anatomy, which is essential for pinpointing any abnormalities causing OSA.
Polysomnography
This test involves monitoring a patient’s sleep behavior and vital signs to measure their sleep quality. It can help detect snoring, apnea events, body movements, heart rate fluctuations, and oxygen levels while you sleep.
Endoscopy
During an endoscopy, a thin tube with a tiny camera at the end is inserted into your throat. This test can help determine if you have excess tissue in your airway that could be causing obstruction and blocking your breathing.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be recommended for those with OSA to check for underlying conditions such as diabetes or hypothyroidism. Your doctor may also order tests to measure electrolyte levels and other hormones that can affect sleep quality. These tests will help provide a better picture of what’s happening inside your body and how it may contribute to your OSA symptoms.
Pulse Oximetry
Pulse oximetry measures your heart rate and oxygen levels during sleep. It can help diagnose OSA by showing how often you stop breathing at night and how much oxygen your body receives while sleeping. This test can also monitor the effectiveness of any treatment you use to manage OSA symptoms.
In Summary
Managing an OSA diagnosis can involve various lifestyle changes and medical interventions. You can reduce your symptoms and improve your overall health and well-being by using a CPAP machine, practicing good sleep hygiene, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and getting regular screenings. Remember to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a management plan tailored to your needs and preferences.